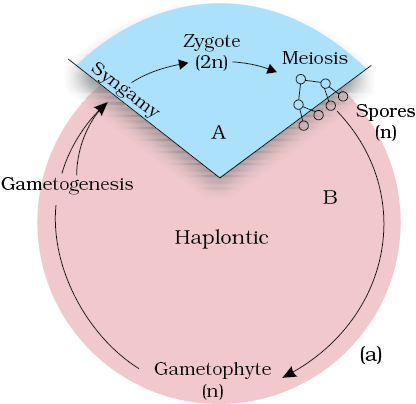
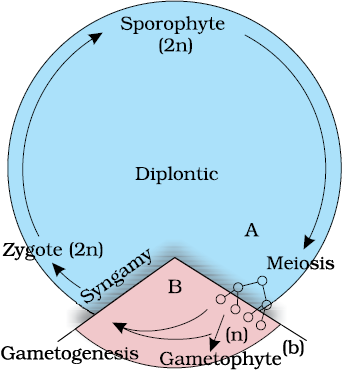
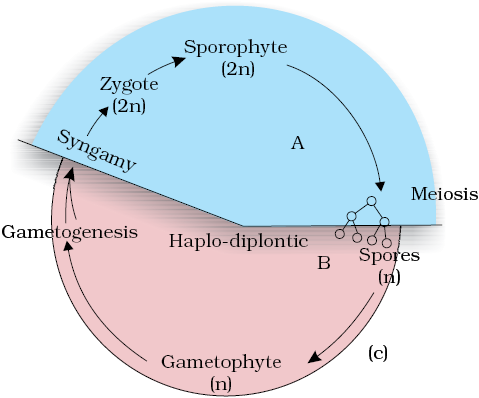
Figure 3.7 Life cycle patterns : (a) Haplontic (b) Diplontic (c) Haplo-diplontic
1. Sporophytic generation is represented only by the one-celled zygote. There are no free-living sporophytes. Meiosis in the zygote results in the formation of haploid spores. The haploid spores divide mitotically and form the gametophyte. The dominant, photosynthetic phase in such plants is the free-living gametophyte. This kind of life cycle is termed as haplontic. Many algae such as Volvox, Spirogyra and some species of Chlamydomonas represent this pattern (Figure 3.7 a).
2. On the other extreme, is the type wherein the diploid sporophyte is the dominant, photosynthetic, independent phase of the plant. The gametophytic phase is represented by the single to few-celled haploid gametophyte. This kind of life cycle is termed as diplontic. An alga, Fucus sp., represents this pattern (Fig. 3.7b). In addition, all seed bearing plants i.e., gymnosperms and angiosperms, follow this pattern with some variations, wherein, the gametophytic phase is few to multi-celled.
3. Bryophytes and pteridophytes, interestingly, exhibit an intermediate condition (Haplo-diplontic); both phases are multicellular. However, they differ in their dominant phases.
A dominant, independent, photosynthetic, thalloid or erect phase is represented by a haploid gametophyte and it alternates with the short-lived multicelluler sporophyte totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte for its anchorage and nutrition. All bryophytes represent this pattern.
The diploid sporophyte is represented by a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, vascular plant body. It alternates with multicellular, saprophytic/autotrophic, independent but short-lived haploid gametophyte. Such a pattern is known as haplo-diplontic life cycle. All pteridophytes exhibit this pattern (Figure 3.7 c).
Interestingly, while most algal genera are haplontic, some of them such as Ectocarpus, Polysiphonia, kelps are haplo-diplontic. Fucus, an alga is diplontic.
Plant kingdom includes algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms. Algae are chlorophyll-bearing simple, thalloid, autotrophic and largely aquatic organisms. Depending on the type of pigment possesed and the type of stored food, algae are classfied into three classes, namely Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae and Rhodophyceae. Algae usually reproduce vegetatively by fragmentation, asexually by formation of different types of spores and sexually by formation of gametes which may show isogamy, anisogamy or oogamy.
Bryophytes are plants which can live in soil but are dependent on water for sexual reproduction. Their plant body is more differentiated than that of algae. It is thallus-like and prostrate or erect and attached to the substratum by rhizoids. They possess root-like, leaf-like and stem-like structures. The bryophytes are divided into liverworts and mosses. The plant body of liverworts is thalloid and dorsiventral whereas mosses have upright, slender axes bearing spirally arranged leaves. The main plant body of a bryophyte is gamete-producing and is called a gametophyte. It bears the male sex organs called antheridia and female sex organs called archegonia. The male and female gametes produced fuse to form zygote which produces a multicellular body called a sporophyte. It produces haploid spores. The spores germinate to form gametophytes.
In pteridophytes the main plant is a sporophyte which is differentiated into true root, stem and leaves. These organs possess well-differentiated vascular tissues. The sporophytes bear sporangia which produce spores. The spores germinate to form gametophytes which require cool, damp places to grow. The gametophytes bear male and female sex organs called antheridia and archegonia, respectively. Water is required for transfer of male gametes to archegonium where zygote is formed after fertilisation. The zygote produces a sporophyte.
The gymnosperms are the plants in which ovules are not enclosed by any ovary wall. After fertilisation the seeds remain exposed and therefore these plants are called naked-seeded plants. The gymnosperms produce microspores and megaspores which are produced in microsporangia and megasporangia borne on the sporophylls. The sporophylls – microsporophylls and megasporophylls – are arranged spirally on axis to form male and female cones, respectively. The pollen grain germinates and pollen tube releases the male gamete into the ovule, where it fuses with the egg cell in archegonia. Following fertilisation, the zygote develops into embryo and the ovules into seeds.
In angiosperms, the male sex organs (stamen) and female sex organs (pistil) are borne in a flower. Each stamen consists of a filament and an anther. The anther produces pollen grains (male gametophyte) after meiosis. The pistil consists of an ovary enclosing one to many ovules. Within the ovule is the female gametophyte or embryo sac which contains the egg cell. The pollen tube enters the embryo-sac where two male gametes are discharged. One male gamete fuses with egg cell (syngamy) and other fuses with diploid secondary nucleus (triple fusion). This phenomenon of two fusions is called double fertilisation and is unique to angiosperms. The angiosperms are divided into two classes – the dicotyledons and the monocotyledons.
During the life cycle of any sexually reproducing plant, there is alternation of generations between gamete producing haploid gametophyte and spore producing diploid sporophyte. However, different plant groups as well as individuals may show different patterns of life cycles – haplontic, diplontic or intermediate.