They are marine animals with streamlined body and have cartilaginous endoskeleton
(Figure 4.19). Mouth is located ventrally. Notochord is persistent throughout life. Gill slits are separate and without operculum (gill cover). The skin is tough, containing minute placoid scales. Teeth are modified placoid scales which are backwardly directed. Their jaws are very powerful. These animals are predaceous. Due to the absence of air bladder, they have to swim constantly to avoid sinking. Heart is two-chambered (one auricle and one ventricle). Some of them have electric organs (e.g., Torpedo) and some possess poison sting (e.g., Trygon). They are cold-blooded (poikilothermous) animals, i.e., they lack the capacity to regulate their body temperature. Sexes are separate. In males pelvic fins bear claspers. They have internal fertilisation and many of them are viviparous.
Examples: Scoliodon (Dog fish), Pristis (Saw fish), Carcharodon (Great white shark), Trygon (Sting ray).

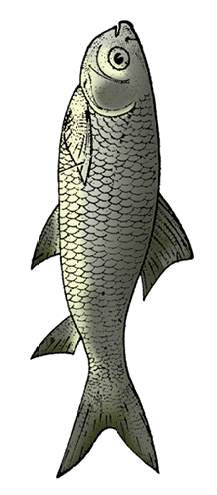
It includes both marine and fresh water fishes with bony endoskeleton. Their body is streamlined. Mouth is mostly terminal (Figure 4.20). They have four pairs of gills which are covered by an operculum on each side. Skin is covered with cycloid/ctenoid scales. Air bladder is present which regulates buoyancy. Heart is two-chambered (one auricle and one ventricle). They are cold-blooded animals. Sexes are separate. Fertilisation is usually external. They are mostly oviparous and development is direct.
Examples: Marine – Exocoetus (Flying fish), Hippocampus (Sea horse); Freshwater – Labeo (Rohu), Catla (Katla), Clarias (Magur); Aquarium – Betta (Fighting fish), Pterophyllum (Angel fish).

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.