The wide range in the structure of higher plants will never fail to fascinate us. Even though the angiosperms show such a large diversity in external structure or morphology, they are all characterised by presence of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits.
In chapters 2 and 3, we talked about classification of plants based on morphological and other characteristics. For any successful attempt at classification and at understanding any higher plant (or for that matter any living organism) we need to know standard technical terms and standard definitions. We also need to know about the possible variations in different parts, found as adaptations of the plants to their environment, e.g., adaptions to various habitats, for protection, climbing, storage, etc.
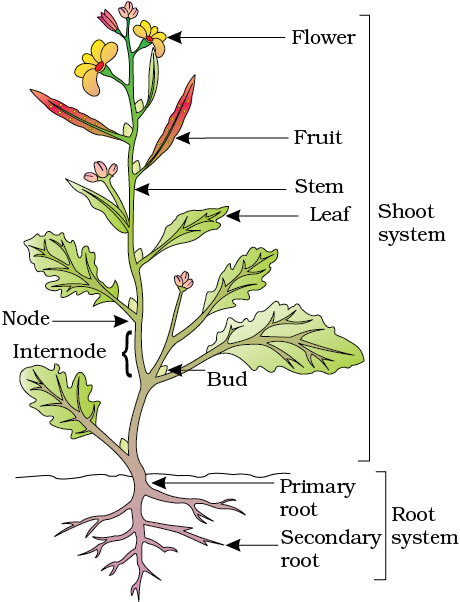
If you pull out any weed you will see that all of them have roots, stems and leaves. They may be bearing flowers and fruits. The underground part of the flowering plant is the root system while the portion above the ground forms the shoot system (Figure 5.1).
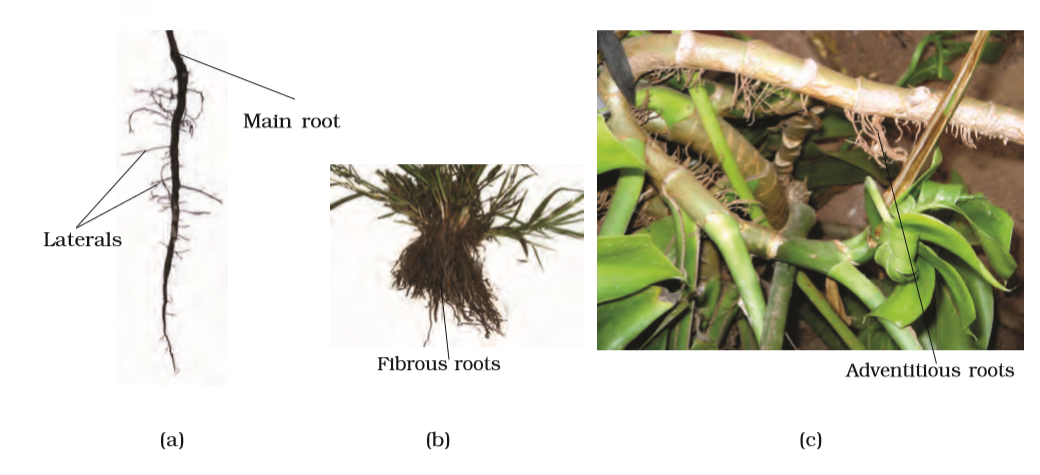
In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil.
It bears lateral roots of several orders that are referred to as secondary, tertiary, etc. roots. The primary roots and its branches constitute the tap root system, as seen in the mustard plant (Figure 5.2a). In monocotyledonous plants, the primary root is short lived and is replaced by a large number of roots. These roots originate from the base of the stem and constitute the fibrous root system, as seen in the wheat plant (Figure 5.2b). In some plants, like grass, Monstera and the banyan tree, roots arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle and are called adventitious roots (Figure 5.2c). The main functions of the root system are absorption of water and minerals from the soil, providing a proper anchorage to the plant parts, storing reserve food material and synthesis of plant growth regulators.