This family was earlier called Papilionoideae, a subfamily of family Leguminosae. It is distributed all over the world (Figure 5.21).
Vegetative Characters
Trees, shrubs, herbs; root with root nodules
Stem: erect or climber
Leaves: alternate, pinnately compound or simple; leaf base, pulvinate; stipulate; venation reticulate.
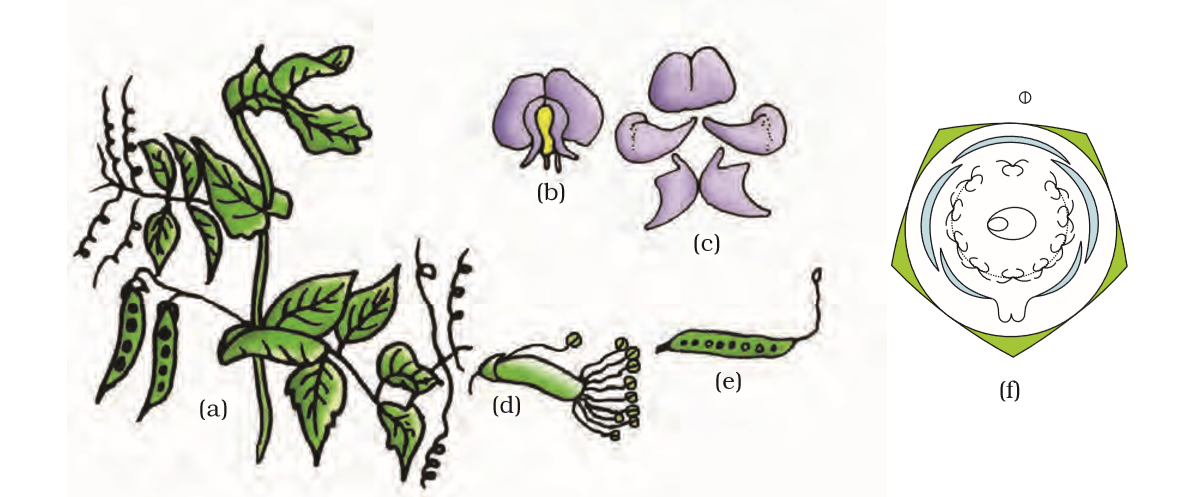
Figure 5.21 Pisum sativum (pea) plant : (a) Flowering twig (b) Flower (c) Petals (d) Reproductive parts (e) L.S.carpel (f) Floral diagram
Floral characters
Inflorescence: racemose
Flower: bisexual, zygomorphic
Calyx: sepals five, gamosepalous; valvate/imbricate aestivation
Corolla: petals five, polypetalous, papilionaceous, consisting of a posterior standard, two lateral wings, two anterior ones forming a keel (enclosing stamens and pistil), vexillary aestivation
Androecium: ten, diadelphous, anther dithecous
Gynoecium: ovary superior, mono carpellary, unilocular with many ovules, style single
Fruit: legume; seed: one to many, non-endospermic
Floral formula: % 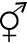
Economic importance
Many plants belonging to the family are sources of pulses (gram, arhar, sem, moong, soyabean; edible oil (soyabean, groundnut); dye (Indigofera); fibres (sunhemp); fodder (Sesbania, Trifolium), ornamentals (lupin, sweet pea); medicine (muliathi).

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.