It is a large family, commonly called as the ‘potato family’. It is widely distributed in tropics, subtropics and even temperate zones (Figure 5.22).
Vegetative Characters
Plants mostly herbs, shrubs and rarely small trees
Stem: herbaceous rarely woody, aerial; erect, cylindrical, branched, solid or hollow, hairy or glabrous, underground stem in potato (Solanum tuberosum)
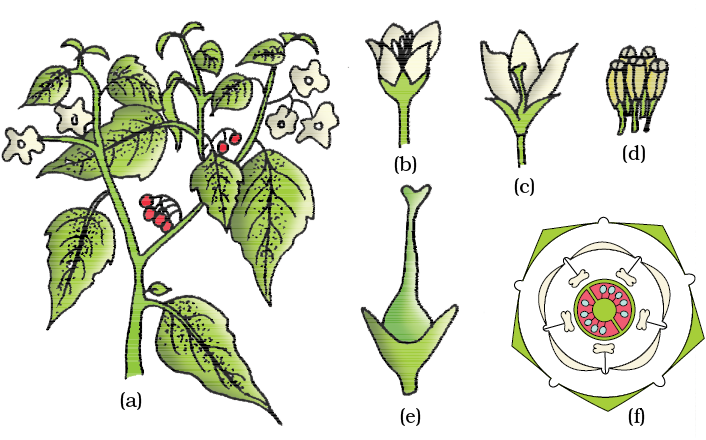
Figure 5.22 Solanum nigrum (makoi) plant : (a) Flowering twig (b) Flower (c) L.S. of flower (d) Stamens (e) Carpel (f) Floral diagram
Leaves: alternate, simple, rarely pinnately compound, exstipulate; venation reticulate
Floral Characters
Inflorescence : Solitary, axillary or cymose as in Solanum
Flower: bisexual, actinomorphic
Calyx: sepals five, united, persistent, valvate aestivation
Corolla: petals five, united; valvate aestivation
Androecium: stamens five, epipetalous
Gynoecium: bicarpellary obligately placed, syncarpous; ovary superior, bilocular, placenta swollen with many ovules, axile
Fruits: berry or capsule
Seeds: many, endospermous
Floral Formula: 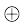
Economic Importance
Many plants belonging to this family are source of food (tomato, brinjal, potato), spice (chilli); medicine (belladonna, ashwagandha); fumigatory (tobacco); ornamentals (petunia).

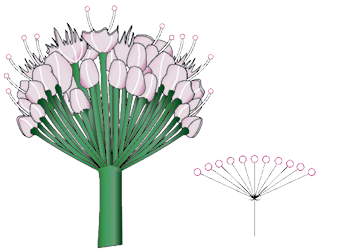


Figure 5.23 Allium cepa (onion) plant : (a) Plant (b) Inflorescence (c) Flower (d) Floral diagram

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.