This is the most dramatic period of the cell cycle, involving a major reorganisation of virtually all components of the cell. Since the number of chromosomes in the parent and progeny cells is the same, it is also called as equational division. Though for convenience mitosis has been divided into four stages of nuclear division (karyokinesis), it is very essential to understand that cell division is a progressive process and very clear-cut lines cannot be drawn between various stages. Karyokinesis involves following four stages:
Prophase which is the first stage of karyokinesis of mitosis follows the S and G2 phases of interphase. In the S and G2 phases the new DNA molecules formed are not distinct but intertwined. Prophase is marked by the initiation of condensation of chromosomal material. The chromosomal material becomes untangled during the process of chromatin condensation (Figure 10.2 a). The centrosome, which had undergone duplication during S phase of interphase, now begins to move towards opposite poles of the cell. The completion of prophase can thus be marked by the following characteristic events:
Chromosomal material condenses to form compact mitotic chromosomes. Chromosomes are seen to be composed of two chromatids attached together at the centromere.
Centrosome which had undergone duplication during interphase, begins to move towards opposite poles of the cell. Each centrosome radiates out microtubules called asters. The two asters together with spindle fibres forms mitotic apparatus.
Cells at the end of prophase, when viewed under the microscope, do not show golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and the nuclear envelope.
The complete disintegration of the nuclear envelope marks the start of the second phase of mitosis, hence the chromosomes are spread through the cytoplasm of the cell. By this stage, condensation of chromosomes is completed and they can be observed clearly under the microscope. This then, is the stage at which morphology of chromosomes is most easily studied. At this stage, metaphase chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids, which are held together by the centromere (Figure 10.2 b). Small disc-shaped structures at the surface of the centromeres are called kinetochores. These structures serve as the sites of attachment of spindle fibres (formed by the spindle fibres) to the chromosomes that are moved into position at the centre of the cell. Hence, the metaphase is characterised by all the chromosomes coming to lie at the equator with one chromatid of each chromosome connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibres from one pole and its sister chromatid connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibres from the opposite pole (Figure 10.2 b).
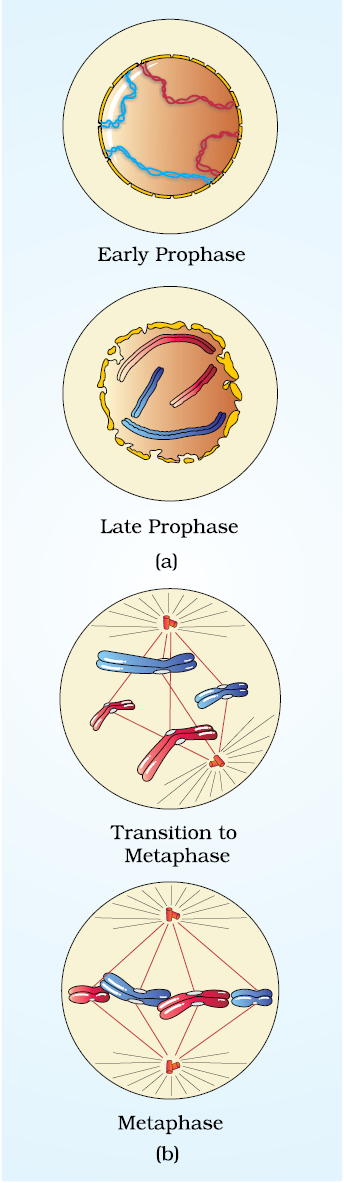
Figure 10.2 a and b : A diagrammatic view of stages in mitosis
The plane of alignment of the chromosomes at metaphase is referred to as the metaphase plate. The key features of metaphase are: