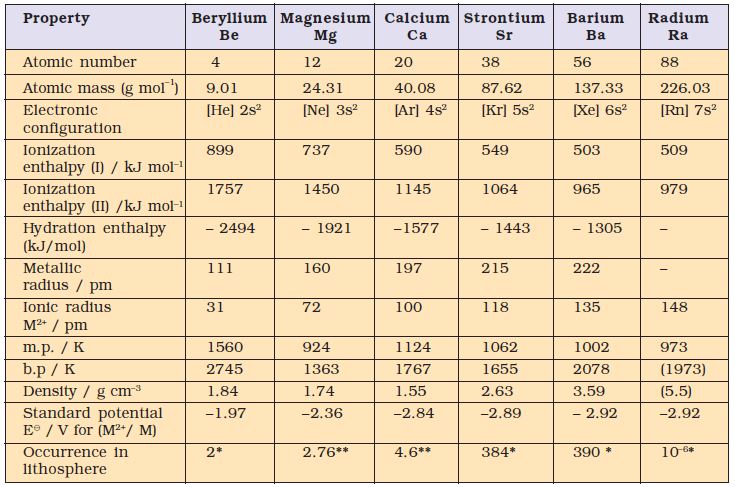
The group 2 elements comprise beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and radium. They follow alkali metals in the periodic table. These (except beryllium) are known as alkaline earth metals. The first element beryllium differs from the rest of the members and shows diagonal relationship to aluminium. The atomic and physical properties of the alkaline earth metals are shown in Table 10.2.
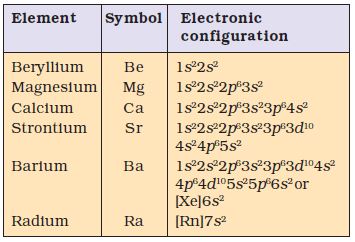
These elements have two electrons in the s -orbital of the valence shell (Table 10.2). Their general electronic configuration may be represented as [noble gas] ns2. Like alkali metals, the compounds of these elements are also predominantly ionic.
10.6.2 Atomic and Ionic Radii
The atomic and ionic radii of the alkaline earth metals are smaller than those of the corresponding alkali metals in the same periods. This is due to the increased nuclear charge in these elements. Within the group, the atomic and ionic radii increase with increase in atomic number.
Table 10.2 Atomic and Physical Properties of the Alkaline Earth Metals
*ppm (part per million); ** percentage by weight
The alkaline earth metals have low ionization enthalpies due to fairly large size of the atoms. Since the atomic size increases down the group, their ionization enthalpy decreases (Table 10.2). The first ionisation enthalpies of the alkaline earth metals are higher than those of the corresponding Group 1 metals. This is due to their small size as compared to the corresponding alkali metals. It is interesting to note that the second ionisation enthalpies of the alkaline earth metals are smaller than those of the corresponding alkali metals.
Like alkali metal ions, the hydration enthalpies of alkaline earth metal ions decrease with increase in ionic size down the group.
Be2+> Mg2+ > Ca2+ > Sr2+ > Ba2+
The hydration enthalpies of alkaline earth metal ions are larger than those of alkali metal ions. Thus, compounds of alkaline earth metals are more extensively hydrated than those of alkali metals, e.g., MgCl2 and CaCl2 exist as MgCl2.6H2O and CaCl2· 6H2O while NaCl and KCl do not form such hydrates.

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.