(a) Alicyclic compounds
Alicyclic (aliphatic cyclic) compounds contain carbon atoms joined in the form of a ring (homocyclic).

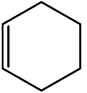
Cyclopropane Cyclohexane Cyclohexene
Sometimes atoms other than carbon are also present in the ring (heterocylic). Tetrahydrofuran given below is an example of this type of compound:
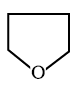
Tetrahydrofuran
These exhibit some of the properties similar to those of aliphatic compounds.
(b) Aromatic compounds
Aromatic compounds are special types of compounds. You will learn about these compounds in detail in Unit 13. These include benzene and other related ring compounds (benzenoid). Like alicyclic compounds, aromatic comounds may also have hetero atom in the ring. Such compounds are called hetrocyclic aromatic compounds. Some of the examples of various types of aromatic compounds are:
Benzenoid aromatic compounds
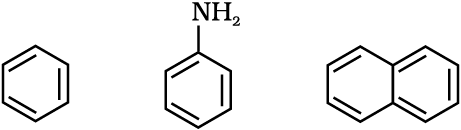
Benzene Aniline Naphthalene
Non-benzenoid compound

Tropone
Heterocyclic aromatic compounds
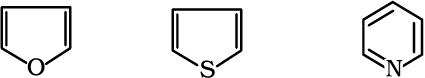
Furan Thiophene Pyridine
Organic compounds can also be classified on the basis of functional groups, into families or homologous series.
The functional group is an atom or a group of atoms joined to the carbon chain which is responsible for the characteristic chemical properties of the organic compounds. The examples are hydroxyl group (–OH), aldehyde group (–CHO) and carboxylic acid group (–COOH) etc.

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.