Benzene was considered as parent ‘aromatic’ compound. Now, the name is applied to all the ring systems whether or not having benzene ring, possessing following characteristics.
(i) Planarity
(ii) Complete delocalisation of the π electrons in the ring
(iii) Presence of (4n + 2) π electrons in the ring where n is an integer (n = 0, 1, 2, . . .).
This is often referred to as Hückel Rule.
Some examples of aromatic compounds are given below:
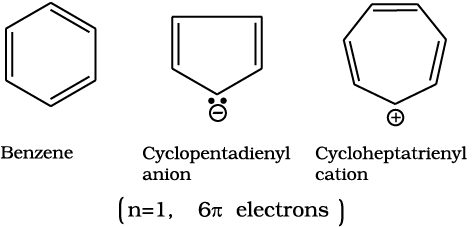
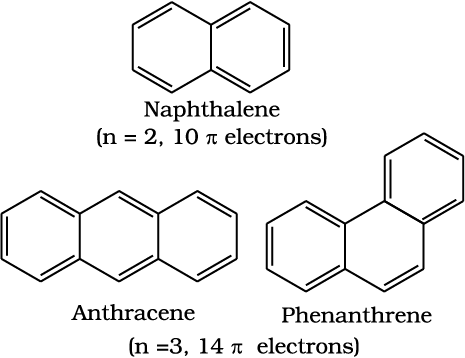
Benzene is commercially isolated from coal tar. However, it may be prepared in the laboratory by the following methods.
(i) Cyclic polymerisation of ethyne: (Section 13.4.4)
(ii) Decarboxylation of aromatic acids: Sodium salt of benzoic acid on heating with sodalime gives benzene.
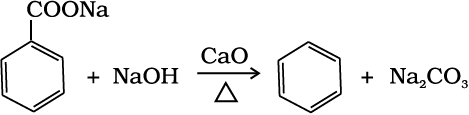 (13.70)
(13.70)
(iii) Reduction of phenol: Phenol is reduced to benzene by passing its vapours over heated zinc dust
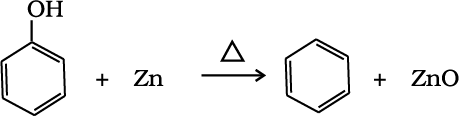 (13.71)
(13.71)

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.