The quantities of heat required to raise the temperature of two solid copper spheres of radii \(r_1\) and \(r_2\) \((r_1=1.5~r_2)\) through \(1~\text{K}\) are in the ratio:
| 1. | \(\dfrac{9}{4}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{5}{3}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{27}{8}\) |

1. \(25^\circ\text C,~75^\circ\text C\)
2. \(40^\circ\text C,~60^\circ\text C\)
3. \(20^\circ\text C,~80^\circ\text C\)
4. \(30^\circ\text C,~70^\circ\text C\)

| 1. | \(45^\circ \text{C}\) | 2. | \(60^\circ \text{C}\) |
| 3. | \(30^\circ \text{C}\) | 4. | \(20^\circ \text{C}\) |
| 1. | \(12^\circ \text{C}\) | 2. | \(50^\circ \text{C}\) |
| 3. | \(73^\circ \text{C}\) | 4. | \(88.5^\circ \text{C}\) |
In the Arctic region, hemispherical houses called Igloos are made of ice. It is possible to maintain a temperature inside an Igloo as high as \(20^\circ \text{C}\) because:
| 1. | ice has a high thermal conductivity. |
| 2. | ice has low thermal conductivity. |
| 3. | ice has a high specific heat. |
| 4. | ice has a higher density than water. |
A deep rectangular pond of surface area \(A\), containing water (density = \(\rho,\) specific heat capacity = \(s\)), is located in a region where the outside air temperature is at a steady value of \(-26^{\circ}\text{C}\). The thickness of the ice layer in this pond at a certain instant is \(x\). Taking the thermal conductivity of ice as \(k\), and its specific latent heat of fusion as \(L\), the rate of increase of the thickness of the ice layer, at this instant, would be given by:
| 1. | \(\dfrac{26k}{x\rho L-4s}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{26k}{x^2\rho L}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{26k}{x\rho L}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{26k}{x\rho L+4s}\) |
What is the temperature of the steel-copper junction in the steady-state of the system shown in the figure? The length of the steel rod = \(15.0\) cm, length of the copper rod = \(10.0\) cm, temperature of the furnace = \(300^{\circ}\text{C}\), temperature of the other end = \(0^{\circ}\text{C}\). The area of the cross section of the steel rod is twice that of the copper rod. (Thermal conductivity of steel = \(50.2 ~\text{J s}^{-1}\text{m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1};\) and of copper \(= 385~\text{J s}^{-1}\text{m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1})\).
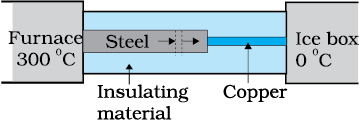
1. \(44.4^{\circ}\text{C}\)
2. \(44.4~\text{K}\)
3. \(54.4^{\circ}\text{C}\)
4. \(54.4~\text{K}\)
| Assertion (A): | Houses made of concrete roofs overlaid with foam keep the room hotter during summer. |
| Reason (R): | The layer of foam insulation prohibits heat transfer, as it contains air pockets. |
Choose the correct option from the given ones:
| 1. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 2. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
| 3. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (R). |
An iron bar \(K_1 = 79~\text{W m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) and a brass bar \(K_2 = 109~\text{W m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) are soldered end to end as shown in the figure. The free ends of the iron bar and brass bar are maintained at \(373\) K and \(273\) K respectively. Then the equivalent thermal conductivity of the compound bar is:
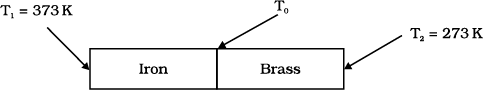
| 1. | \(94.6~\text{W m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) | 2. | \(93.6~\text{W m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) |
| 3. | \(81.6~\text{W m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) | 4. | \(91.6~\text{W m}^{-1}\text{K}^{-1}\) |
Radius of a conductor increases uniformly from left end to right end as shown in the figure.
The material of the conductor is isotropic and its curved surface is thermally isolated from its surrounding. Its ends are maintained at temperatures \(T_1\) and \(T_2~(T_1>T_2).\) If in steady state, heat flow rate is equal to \(H,\) then which of the following graphs is correct?
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |







