Listed in the table are forward and reverse rate constants for the reaction
2N0(g) (g) + (g)
|
Temperature |
||||
| 1400 | 0.29 | 1.1 | ||
| 1500 | 1.3 | 1.4 |
Select the correct statement :
1. Reaction is exothermic and value of equilibrium constant () at 1400 K is 3.79x
2. Reaction is endothermic and value of at 1400 K is 2.63x
3. Reaction is exothermic and value of at 1400 K is 2.63 X
4. Reaction is endothermic and value of at 1500 K is 9.28 x
Consider a reaction \(A(g) \xrightarrow { k=0.1 M m^{-1}}2B(g)\). If initial concentration of A is 0.5 M then select graph.
| 1. | 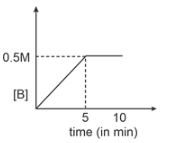 |
2. | 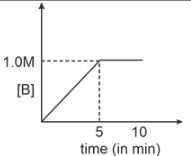 |
| 3. | 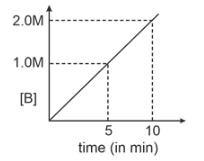 |
4. | 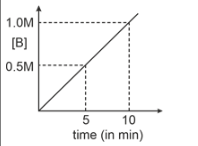 |
A graph between log and log a (abscissa), a being the initial
concentration of A in the reaction. For reaction AProduct, the rate law is :
| 1. | \(\frac{-d A}{d t}=\mathrm{K}\) | 2. | \(\frac{-d A}{d t}=K A\) |
| 3. | \(\frac{-d A}{d t}=K A^2\) | 4. | \(\frac{-d A}{d t}=K A^3\) |
If ‘a’ is the initial concentration of the reactant, the half-period of the reaction
of order Is inversely proportional to:
1.
2.
3.
4.
In the following reaction AB + C, rate constant is 0.001 . If we start with 1
M of A then conc. of A and B after 10 minutes are respectively:
1. 0.5 M, 0.5 M
2. 0.6 M, 0.4M
3. 0.4 M, 0.6M
4. None of these
Half life () and completion time (T) of the above reaction (A2B) are:
1. 500min, 750 min
2. 500 sec. 750 sec
3. 500 sec, 1000 sec
4. None of these
For the zero-order reaction A B + C; initial concentration of A is 0.1 M. If A = 0.08 M after 10 minutes, then it's half-life and completion time are respectively:
1. 10 min; 20 min
2. 2x m; 4x min;
3. 25 min, 50 min
4. 250 min, 500 min
The decomposition of azo methane, at certain temperature according to the
equation is a first order reaction. After 40 minutes from the start, the total pressure developed is found to be 350 mm Hg in place of initial pressure 200 mm Hg of azo methane. The value of rate constant k is:
1. 2.88 sec-1
2. 1.25 sec’
3. 5.77 sec
4. None of these
For a complex reaction A products = 180 kJ/mol; = 80 kJ/mol; =
50 kJ/mol Overall rate constant k is related to individual rate constant by the equation
Activation energy (kJ/mol) for overall reaction is:
1. 100
2. 43.44
3. 150
4. 140
For reaction AB, the rate constant = and for the reaction X Y, the rate constant = . If = , = , Ea1= 600 cal/mol and = 1200 cal/mol, then the temperature at which = is: (Given; R = 2 cal/K-mol)
1. 300 K
2. 300 \(\times\) 2.303 K
3.
4. None of these
A catalyst lowers the activation energy for a certain reaction from 83.314 m to
75 kJ at 500 K. What will be the rate of reaction as compare to uncatalysed reaction ? Assume other things being equal
1. Double
2. 28 times
3. 7.38 times
4. 7.38 X times
A radioactive sample had an initial activity of 56 dpm. After 69.3 minutes,
it was found to have an activity of 28 dpm. Find the number of atoms in a
sample having an activity of 100 dpm
1. 693
2. 100
3. 1000
4. 10,000
has a half life of 22 years. The decays follows two parallel paths 
What are the decay constants () for Th and Fr respectively?
1. 0.03087, 0.00063
2. 0.00063, 0.03087
3. 0.02,0.98
4. None of these
The reaction A(g) + 2B (g) C (g) is an elementary reaction. In an experiment
involving this reaction, the initial partial pressures of A and B are = 0.40 atm
and = 1.0 atm respectively. When = 0.3 atm, the rate of the reaction
relative to the initial rate is:
1.
2.
3.
4. None of these
For a first order homogenous gaseous reaction A 2 B + C If the total pressure after time t was and after long time () was then k in terms of , and t is
1.
2.
3.
4. None of these
Consider the reaction 
The rate constant for two parallel reactions were found to be and 4x . If the corresponding energies of activation of
the parallel reaction are loo and 120 kJ/mol respectively, what is the net energy of activation () of A?
(1) 100 kJ/mol
(2) 120 kJ/mol
(3) 116 kJ/mol
(4) 220 kJ/mol
A reaction takes place in various steps. The rate constant for first, second, third
and fifth steps are , , and respectively. The overall rate constant is
given by
If activation energy are 40, 60, 50 and 10 kJ/mol respectively, the overall
energy of activation (kJ/mol) is :
1. 10
2. 20
3. 25
4. None of these
.
.
.
.
.