In dicot stem the vascular bundle is:-
| 1. | Conjoint, open and with exarch protoxylem. |
| 2. | Conjoint, open and with endarch protoxylem. |
| 3. | Conjoint and closed. |
| 4. | Scattered, each surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath. |
Match each item in Column I with one item in Column II and chose your answer from the codes given below.
|
Column-I |
Column-II (vascular bundle) |
||
| I. | Dicot stem | 1. | Collateral and open |
| II. | Monocot stem | 2. | Collateral and closed |
| III. | Dicot root | 3. | Radial, xylem endarch |
| 4. | Radial, xylem exarch |
Codes:
| I | II | III | |
| 1. | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 2. | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| 3. | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| 4. | 1 | 2 | 4 |
Read the different components from I to IV in the list given below and tell the correct order of the components with reference to their arrangement from outer side to inner side in a woody dicot stem:
I. Secondary cortex
II. Wood
III. Secondary phloem
IV. Phellem
The correct order is:
1. III, IV, II, I
2. I, II, IV, III
3. IV, I, III, II
4. IV, III, I, II
The cells shown in the below diagram are of _______ tissue and can be seen in _______ layer of the dicot stem.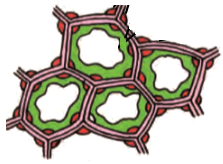
| 1. | Collenchyma, Hypodermis |
| 2. | Sclerenchyma, Sclereids |
| 3. | Parenchyma, Pericycle |
| 4. | Parenchyma, Pith |
In dicot stem epidermis is___________ layered and hypodermis is __________layered
| 1. | single, multi | 2. | multi,single |
| 3. | single, single | 4. | multi,multi |
Which of the following is referred to as the ‘starch sheath’
| 1. | hypodermis | 2. | pericycle |
| 3. | epidermis | 4. | None of these |
In between the vascular bundles, radially placed parenchymatous cells constitute
| 1. | medullary rays | 2. | cortex |
| 3. | medulla | 4. | cortical rays |
In stems the Protoxylem lies toward ______and Metaxylem lies toward the_________ respectively.
(1) Centre, periphery
(2) Periphery, centre
(3) Below, above
(4) Above, below
Hypodermis in dicot stem is composed of
1. Paraenchyma
2. Collenchyma
3. Sclerenchyma
4. Both 1. and 3.
Conjoint open vascular bundles are present in
| 1. | stem of dicots only |
| 2. | stem of dicots and gymnosperms |
| 3. | stem of monocots and gymnosperms |
| 4. | stem of monocots only |
In a dicot stem the term 'starch sheath' is used for:
| 1. | Epidermis with guard cells | 2. | Hypodermis |
| 3. | Endodermis | 4. | Pericycle |
The vascular bundles in a dicot stem are:
| 1. | conjoint, open with endarch protoxylem |
| 2. | conjoint, closed with endarch protoxylem |
| 3. | conjoint, open with exarch protoxylem |
| 4. | conjoint, closed with exarch protoxylem |
The hypodermis of a dicotyledonous stem:
| 1. | is parenchymatous and synthesizes and stores food |
| 2. | is collenchymatous and provides mechanical strength to the young stem |
| 3. | is sclerenchymatous and provides mechanical strength to the young stem |
| 4. | is parenchymatous and provides mechanical strength to the young stem |
The ring arrangement of vascular bundles is a characteristic feature of:
| 1. | Monocot stem | 2. | Dicot stem |
| 3. | Monocot root | 4. | Dicot root |
A conjoint and open vascular bundle will be observed in the transverse section of
| 1. | Monocot root | 2. | Monocot stem |
| 3. | Dicot root | 4. | Dicot stem |
Match the plants in Column-I with the description of anatomy of vascular bundles in them in Column-II and select the correct option from the codes given:
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
||
| A. |
Dicot stem |
a. |
Collateral, closed and scattered in ground tissue |
| B. |
Monocot stem |
b. |
Conjoint, collateral endarch and open |
| C. |
Dicot root |
c. |
Radial, exarch and polyarch [usually more than 6] |
| D. |
Monocot root |
d. |
Radial, exarch and 2 to 6 in number |
Codes:
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | a | b | c | d |
| 2. | b | a | d | c |
| 3. | a | b | d | c |
| 4. | b | a | c | d |
Starch sheath is found in :-
| 1. | Dicot stem | 2. | Monocot stem |
| 3. | Dicot root | 4. | Monocot root |
Conjoint, collateral, open and endarch vascular bundles are found in
| 1. | Monocot stem | 2. | Monocot root |
| 3. | Dicot root | 4. | Dicot stem |
Which of the following is not a correct difference between the anatomy of a dicot stem and a dicot root?
| Feature | Dicot stem | Dicot root | |
| 1. | Epidermal hairs | Present, multicellular trichomes | Present, unicelluar root hairs |
| 2. | Hypodermis | Present, made up of collenchyma | Present, made up of sclerenchyma |
| 3. | Pericycle | Many layered, made up of sclerenchyma | Single layered, madeup of parenchyma |
| 4. | Vascular bundles | 8, Conjoint, collateral and open, Endarch | Eight, four each of xylem and phloem,Radial, Exarch |
Identify the incorrect comparison between monocots and dicots in general:
| Character | Monocots | Dicots | |
| 1. | Leaves | Parallel venation | Reticulate venation |
| 2. | Roots | Primary root of short duration, replaced by adventitial roots forming fibrous or fleshy root systems | Develops from the radicle. Primary root often persists forming strong tap roots and secondary roots |
| 3. | Plant stem: Vascular bundles | Ring of primary bundles with cambium, differentiated into cortex and stele | Numerous scattered bundles in ground parenchyma, cambium mostly absent, no differentiation between cortical and stelar regions |
| 4. | Flowers | Parts in threes (trimerous) or multiples of three | Fours (tetramerous) or fives (pentamerous) |
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A. | Dicot stem | P. | Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring |
| B. | Monocot stem | Q. | Pith is small or inconspicuous |
| C. | Dicot root | R. | Vascular bundles are many and scattered in the ground tissue with no definite arrangement. |
| D. | Monocot root | S. | Pith is large and well developed |
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | Q | S | P | R |
| 2. | S | Q | R | P |
| 3. | P | R | Q | S |
| 4. | R | P | S | Q |

| 1. | Monocot stem | 2. | Dicot stem |
| 3. | Monocot root | 4. | Dicot root |
| Assertion (A): | In the dicot stem, the vascular bundles are open. |
| Reason (R): | Cambium is present between xylem and phloem of the vascular bundle in the dicot stem. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
| 1. | Pith cells |
| 2. | Hypodermal cells |
| 3. | Meristem present in stelar region |
| 4. | Endodermal cells |
| 1. | Dicotyledonous stem |
| 2. | Dicotyledonous root |
| 3. | Monocotyledonous stem |
| 4. | Monocotyledonous root |
| 1. | Hypodermis – Pericycle – Endodermis – Vascular bundles |
| 2. | Vascular bundles – Pericycle – Endodermis – Hypodermis |
| 3. | Hypodermis – Endodermis – Pericycle – Vascular bundles |
| 4. | Vascular bundles – Endodermis – Pericycle – Hypodermis |
| Statement I: | Hypodermis consists of a few layers of collenchymatous cells. |
| Statement II: | The cells of the endodermis are rich in protein granules. |
| Statement III: | Pericycle is in the form of semi-lunar patches of sclerenchyma. |
| Statement IV: | The ‘ring’ arrangement of vascular bundles is a characteristic of dicot stem. |

| 1. | Monocot root | 2. | Monocot stem |
| 3. | Dicot stem | 4. | Dicot root |