A projectile thrown from the ground has horizontal range R. If velocity at the highest point is doubled somehow, the new range will be:
(1) 3 R
(2) 1.5 R
(3) R
(4) 2 R
The time of flights for a particle thrown for equal range at different angles is 4 sec and 3 sec. Speed of projection is:
(1) 10 m/s
(2) 20 m/s
(3) 25 m/s
(4) 50 m/s
A body is projected from the ground at a speed v at an angle above the horizontal. The radius of curvature of its path at the highest point is:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
A particle is projected from the origin with velocity m/s. The acceleration in the region is constant and -10 . The magnitude of velocity after one second is
(1) 8 m/s
(2) m/s
(3) m/s
(4) m/s
The speed of a boat in still water is half of the velocity of the flow of water(v). At what angle boat should steer with the direction of flow of water so that drift of boat is minimum?
(1) 30°
(2) 60°
(3) 90°
(4) 120°
A sports car travels at \(20~\text{m/s}\) along a horizontal road. A camera positioned \(40~\text{m}\) horizontally away from the road (as shown in the diagram) tracks the car at a \(45^\circ\) viewing angle. What angular velocity must the camera rotate at to keep the car in focus?
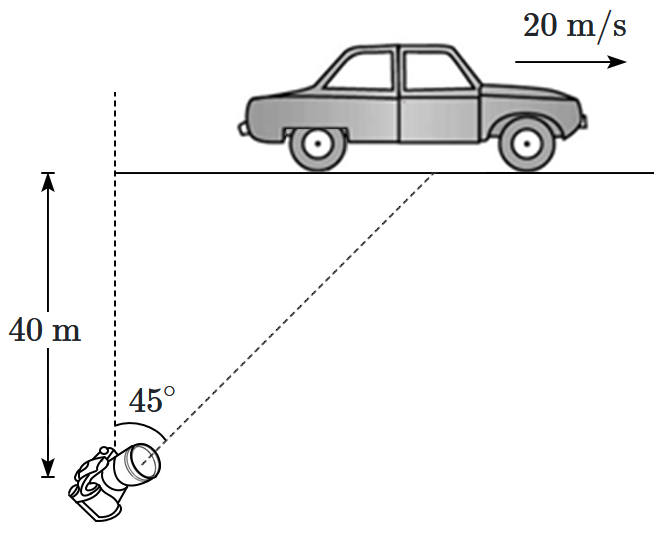
1. \(1.000~\text{rad/s}\)
2. \(0.500~\text{rad/s}\)
3. \(0.250~\text{rad/s}\)
4. \(0.125~\text{rad/s}\)
The magnitude of a vector is constant but it is changing its direction continuously. The angle between and is :
(1) 180°
(2) 120°
(3) 90°
(4) 0°
A particle is moving on a circular path of radius \(R.\) When the particle moves from point \(A\) to \(B\) (angle \( \theta\)), the ratio of the distance to that of the magnitude of the displacement will be:
1. \(\dfrac{\theta}{\sin\frac{\theta}{2}}\)
2. \(\dfrac{\theta}{2\sin\frac{\theta}{2}}\)
3. \(\dfrac{\theta}{2\cos\frac{\theta}{2}}\)
4. \(\dfrac{\theta}{\cos\frac{\theta}{2}}\)
Two particles move from \(A\) to \(C\) and \(A\) to \(D\) on a circle of radius \(R\) and the diameter \(AB.\) If the time taken by both particles is the same, then the ratio of magnitudes of their average velocities is:

1. \(2\)
2. \(2\sqrt{3}\)
3. \(\sqrt{3}\)
4. \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
A particle moves on the curve \(x^2 = 2y\). The angle of its velocity vector with the \(x\)-axis at the point \(\left(1, \frac{1}{2}\right )\) will be:
| 1. | \(30^\circ\) | 2. | \(60^\circ\) |
| 3. | \(45^\circ\) | 4. | \(75^\circ\) |







