An electron beam passes between two parallel plate electrodes as shown in the diagram. The bottom plate is kept at zero potential, while a slowly varying positive voltage is applied to the upper plate, as shown in the graph. After passing between the plates the beam hits a screen and makes spot. Ignoring gravity , the spot is:
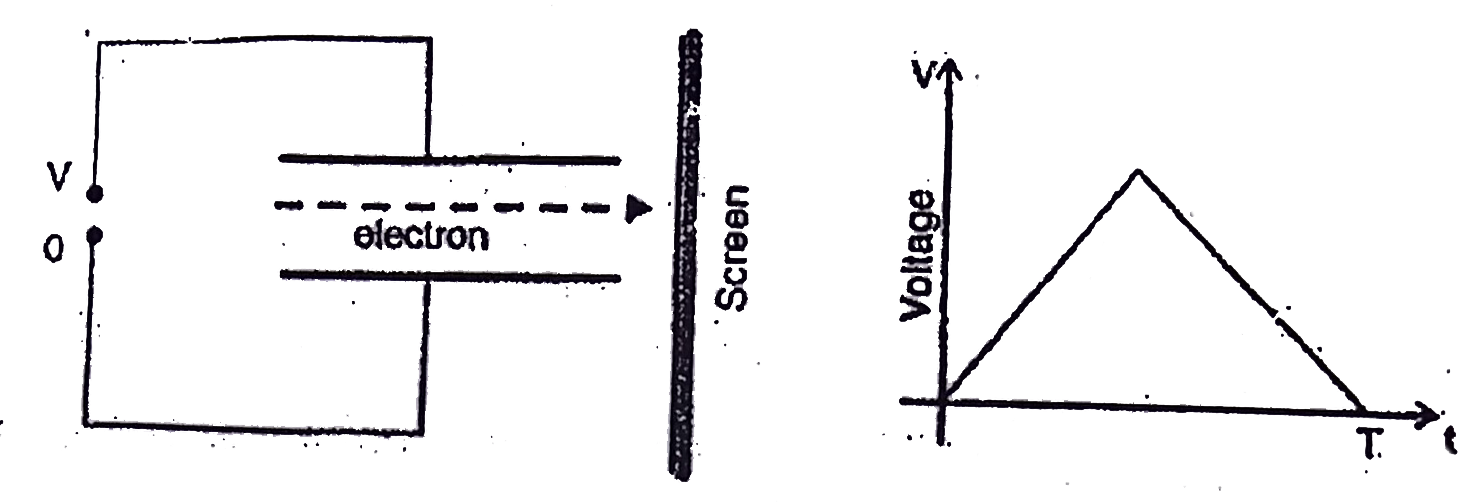
1. deflected up
2. deflected down
3. deflected up then down
4. deflected down then up

A parallel plate capacitor is charged from a cell and then isolated from it. The separation between the plates is now increased.
1. the force of attraction between the plates will increased
2. the field in the region between the plates will not change
3. the energy stored in the capacitor will decrease
4. the potential difference between the plates will decrease
A parallel plate capacitor has a parallel sheet of copper inserted between and parallel to the two plates without touching the plates. The capacity of the capacitor after the introduction of the copper sheet is (Assume thickness of sheet is negligible) -
1. minimum when the copper sheet touches one of the plates.
2. maximum when the copper sheet touches one of the plates
3. does not vary for any positions of the sheet between the plates.
4. lesser than that before introducing the sheet.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by connecting it to a battery. The battery is disconnected and the plates of the capacitor are pulled apart to make the separation between the plates twice. Again the capacitor is connected to the battery (with same polarity) then:
1. Charge from the battery flows into the battery after reconnection.
2. Charge from capacitor flows into the battery after reconnection.
3. The potential difference between the plates decreases when the plates are pulled apart.
4. After reconnection of battery, potential difference between the plates will immediately become half of the initial potential difference (just after disconnecting the battery)
A capacitor C is charged to a potential difference V and battery is disconnected. Now if the capacitor plates are brought close slowly by some distance:
1. some + ve work is done by external agent
2. energy of capacitor will decrease
3. energy of capacitor will increase
4. none of the above
The separation between the plates of a isolated charged parallel plate capacitor is increased. Which of the following quantities will not change?
1. charge on the capacitor
2. potential difference across the capacitor
3. energy of the capacitor
4. energy density between the plates.
An isolated metallic sphere of radius R has an electric charge. It is connected by means of a conducting wire to a distant uncharged metallic sphere of radius r (r<R). Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Total energy of the system must increase
2. Total energy of the system must decrease
3. Final surface charge densities on two spheres may be equal to each other
4. None of these
An uncharged capacitor having capacitance C is connected across a battery of emf . Now the capacitor is disconnected and then reconnected across the same battery but with reversed polarity. Then :
1. after reconnection, work done by the battery is 2C2
2. after reconnection, thermal energy produced in the circuit will be equal to two-third of the total energy supplied by the battery
3. after reconnection, no energy is supplied by the battery
4. after reconnection, half of the energy supplied by the battery is converted into heat.
When a parallel plate capacitor is connected to a source of constant potential difference-
1. all the charge drawn from source is not stored in the capacitor.
2. all the energy drawn from the source is stored in the capacitor.
3. the potential difference across the capacitor grows very rapidly initially and this rate decreases to zero eventually.
4. the capacitance increases with the increase of the charge in the capacitor.
Which of the following statements is true?
1. The capacitance of a capacitor is the magnitude of net charge present on the two plates divided by the potential difference between the plates.
2. The equivalent capacitance of two capacitors in parallel is always the sum of the two capacitances
3. A dielectric material inserted between the conductors of a capacitor decreases its capacitance.
4. The electrostatic energy stored in a capacitor is always more than the energy lost as heat when it is connected across a battery.






