Velocity-time \((v\text-t)\) graph for a moving object is shown in the figure. Total displacement of the object during the time interval when there is non-zero acceleration or retardation is:
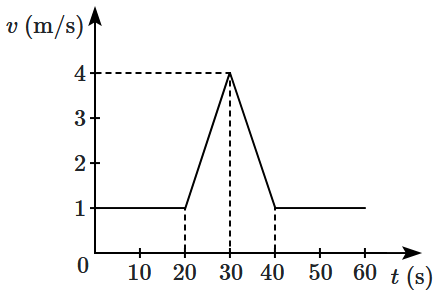
1. \(60~\text{m}\)
2. \(50~\text{m}\)
3. \(30~\text{m}\)
4. \(40~\text{m}\)

1. \(60~\text{m}\)
2. \(50~\text{m}\)
3. \(30~\text{m}\)
4. \(40~\text{m}\)
For the velocity-time graph shown in figure below the distance covered by the body in last two seconds of its motion is what fraction of the total distance covered by it in all the seven seconds
1.
2.
3.
4.
In the following graph, the distance travelled by the body in metres is:
| 1. | \(200\) | 2. | \(250\) |
| 3. | \(300\) | 4. | \(400\) |
Velocity-time curve for a body projected vertically upwards is
1. Parabola
2. Ellipse
3. Hyperbola
4. Straight line
The displacement-time graph of a moving particle is shown below. The instantaneous velocity of the particle is negative at the point
1. D
2. F
3. C
4. E
An object is moving with a uniform acceleration which is parallel to its instantaneous direction of motion. The displacement (s) – velocity (v) graph of this object is
| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |
Which of the following graph represents uniform motion ?
| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |
A ball is dropped vertically from a height \(d\) above the ground. It hits the ground and bounces up vertically to a height \(d/2.\) Neglecting subsequent motion and air resistance, its velocity \(v\) varies with the height \(h\) above the ground is:
| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |
The graph of displacement v/s time is
Its corresponding velocity-time graph will be
1. 
3. 
A train moves from one station to another in 2 hours time. Its speed-time graph during this motion is shown in the figure. The maximum acceleration during the journey is
1. \(140\) km h-2
2. \(160\) km h-2
3. \(100\) km h-2
4. \(120\) km h-2













