Two containers of equal volumes contain the same gas at pressures \(P_1\) and \(P_2\) and absolute temperatures \(T_1\) and \(T_2\), respectively. On joining the vessels, the gas reaches a common pressure \(P\) and common temperature \(T\). The ratio \(\dfrac{P}{T}\) is equal to:
1.
\(\dfrac{P_1}{T_1}+\dfrac{P_2}{T_2}\)
2.
\(\dfrac{P_1T_1+P_2T_2}{(T_1+T_2)^2}\)
3.
\(\dfrac{P_1T_2+P_2T_1}{(T_1+T_2)^2}\)
4.
\(\dfrac{P_1}{2T_1}+\dfrac{P_2}{2T_2}\)
At the top of a mountain, a thermometer reads \(7^\circ \text{C}\) and a barometer reads \(70\) cm of mercury. At the bottom of the mountain, the thermometer reads \(27^\circ \text{C},\) and the barometer reads \(76\) cm of mercury.
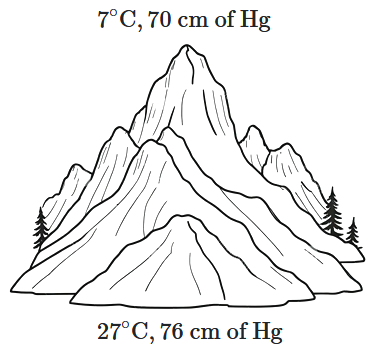
What is the comparison (ratio) of the air density at the top of the mountain to that at the bottom?
| 1. | \(\dfrac{75}{76}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{70}{76}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{76}{75}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{76}{70}\) |
A vessel is partitioned in two equal halves by a fixed diathermic separator. Two different ideal gases are filled in left (L) and right (R) halves. The rms speed of the molecules in L part is equal to the mean speed of molecules in the R part. Then the ratio of the mass of a molecule in L part to that of a molecule in R part is
1.
2.
3.
4.
A gas is filled in the cylinder shown in the figure. The two pistons are joined by a string. If the gas is heated, the pistons will
1.Move towards left
2. Move towards right
3. Remain stationary
4. None of these
A closed vessel contains 8gm of oxygen and 7gm of nitrogen. The total pressure is 10 atm at a given temperature. If now oxygen is absorbed by introducing a suitable absorbent the pressure of the remaining gas in atm will be
1. 2
2. 10
3. 4
4. 5
is a triatomic gas. Mean kinetic energy of one gram gas will be (If N-Avogadro's number, k-Boltzmann's constant and molecular weight of , Degree of freedom f = 7)
1.
2.
3.
4.
40 calories of heat is needed to raise the temperature of 1 mole of an ideal monoatomic gas from 20°C to 30°C at a constant pressure. The amount of heat required to raise its temperature over the same interval at a constant volume is
1. 20 calorie
2. 40 calorie
3. 60 calorie
4. 80 calorie
The pressure and volume of saturated water vapour are P and V respectively. It is compressed isothermally thereby volume becomes V/2, the final pressure will be
1. More than 2P
2. P
3. 2P
4. 4P
If the intermolecular forces vanish away, the volume occupied by the molecules contained in 4.5 kg water at standard temperature and pressure will be
1.
2.
3.
4.
When an air bubble of radius ‘r’ rises from the bottom to the surface of a lake, its radius becomes 5r/4 (the pressure of the atmosphere is equal to the 10 m height of water column). If the temperature is constant and the surface tension is neglected, the depth of the lake is
1. 3.53 m
2. 6.53 m
3. 9.53 m
4. 12.53 m








