A current loop in a magnetic field:
1.
can be in equilibrium in one orientation
2.
can be in equilibrium in two orientations, both the equilibrium states are unstable
3.
can be in equilibrium in two orientations, one stable while the other is unstable
4.
experiences a torque whether the field is uniform or non-uniform in all orientations
| 1. | can be in equilibrium in one orientation |
| 2. | can be in equilibrium in two orientations, both the equilibrium states are unstable |
| 3. | can be in equilibrium in two orientations, one stable while the other is unstable |
| 4. | experiences a torque whether the field is uniform or non-uniform in all orientations |
A very long straight wire carries a current I. At the instant when a charge +Q at point P has velocity , as shown, the force on the charge is-
1. Along OX
2. Opposite to OY
3. Along OY
4. Opposite to OX
A uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field are acting in the same direction in a certain region. If an electron is projected in the region such that its velocity is pointed along the direction of fields, then the electron:
| 1. | speed will decrease |
| 2. | speed will increase |
| 3. | will turn towards the left of the direction of motion |
| 4. | will turn towards the right of the direction of motion |
Two charged particles having charges q and mass m are moving on circular paths in same uniform magnetic field with speed v and 2v. Ratio of their angular velocities are
1.
2.
3.
4.
A circular current-carrying coil has a radius \(R.\) The distance from the centre of the coil, on the axis, where \(B\) will be \(\frac18\) of its value at the centre of the coil is:
1. \(\frac{R}{\sqrt3}\)
2. \(\sqrt3R\)
3. \(2\sqrt3R\)
4. \(\frac{2R}{\sqrt3}\)
1. 1 A
2. 58 A
3. 58 mA
4. 30 mA
| 1. | Angle between \(\vec v\) and \(\vec {B}\) is necessarily \(90^{\circ}\). |
| 2. | Angle between \(\vec v\) and \(\vec {B}\) can have any value other than \(90^{\circ}\). |
| 3. | Angle between \(\vec v\) and \(\vec {B}\) can have any value other than zero and \(180^{\circ}\). |
| 4. | Angle between \(\vec v\) and \(\vec {B}\) is either zero or \(180^{\circ}\). |
Magnetic field at point O will be: (assume straight wire segments are infinite)
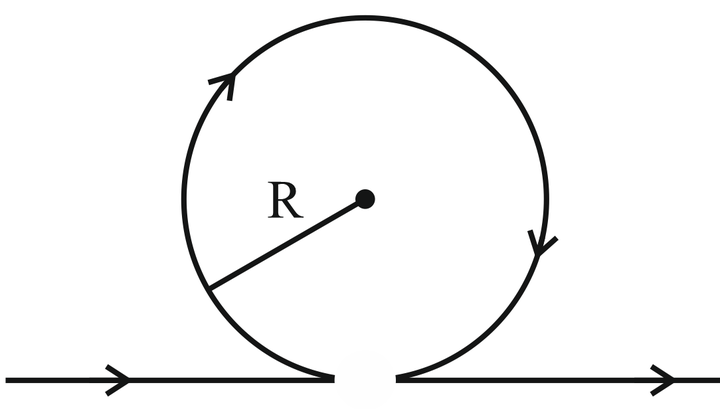
1. \(\frac{\mu_{_0}l}{2R}\) interior
2. \(\frac{\mu_{_0}l}{2R}\) exterior
3. \(\frac{\mu_{_0}l}{2R}1-\frac{l}{\pi}\) interior
4. \(\frac{\mu_{_0}l}{2R}1-\frac{l}{\pi}\) exterior
A square loop is made by a uniform conductor wire as shown in the figure,
The net magnetic field at the centre of the loop if the side length of the square is a:
1. \(\frac{\mu_{_0}i}{2a}\)
2. zero
3. \(\frac{\mu_{_0}i^2}{a^2}\)
4. None of these
| 1. | low resistance in series with its coil |
| 2. | low resistance in parallel with its coil |
| 3. | high resistance in series with its coil |
| 4. | high resistance in parallel with its coil |








