An increase in the temperature of a gas-filled in a container would lead to:
1.
decrease in the intermolecular distance.
2.
increase in its mass.
3.
increase in its kinetic energy.
4.
decrease in its pressure.
Match Column-I and Column-II and choose the correct match from the given choices.
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| (A) | Root mean square speed of gas molecules | (P) | \(\dfrac13nm\bar v^2\) |
| (B) | The pressure exerted by an ideal gas | (Q) | \( \sqrt{\dfrac{3 R T}{M}} \) |
| (C) | The average kinetic energy of a molecule | (R) | \( \dfrac{5}{2} R T \) |
| (D) | The total internal energy of a mole of a diatomic gas | (S) | \(\dfrac32k_BT\) |
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) | |
| 1. | (Q) | (P) | (S) | (R) |
| 2. | (R) | (Q) | (P) | (S) |
| 3. | (R) | (P) | (S) | (Q) |
| 4. | (Q) | (R) | (S) | (P) |
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
1. mass
2. speed
3. momentum
4. kinetic energy
Hydrogen gas is contained in a vessel and the RMS speed of the gas molecules is \(v\). The gas is heated isobarically so that its volume doubles, then it is compressed isothermally so that it returns to the same volume. The final RMS speed of the molecules will be:
| 1. | 2\(v\) | 2. | \(v\)/2 |
| 3. | \(v\)\(\sqrt2\) | 4. | \(v\)/\(\sqrt2\) |
| 1. | mass density, the mass of the gas. |
| 2. | number density, molar mass. |
| 3. | mass density, molar mass. |
| 4. | number density, the mass of the gas. |
The mean free path \(l\) for a gas molecule depends upon the diameter, \(d\) of the molecule as:
| 1. | \(l\propto \dfrac{1}{d^2}\) | 2. | \(l\propto d\) |
| 3. | \(l\propto d^2 \) | 4. | \(l\propto \dfrac{1}{d}\) |
| 1. | 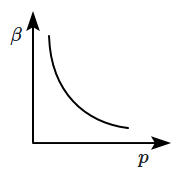 |
2. | 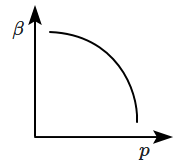 |
| 3. | 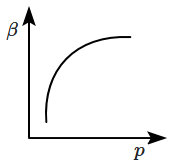 |
4. | 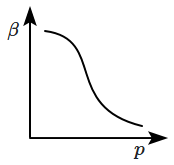 |
If the pressure in a closed vessel is reduced by removing some of the gas, how is the mean free path between two gas molecules affected?
| 1. | It increases. |
| 2. | It decreases. |
| 3. | It remains unchanged. |
| 4. | It increases or decreases depending on the nature of the gas. |
| 1. | \(T_\mathrm {H_{2}}=T_\mathrm{H e}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{T_\mathrm{H_2}}{2}=\dfrac{T_\mathrm{He}}{4}\) |
| 3. | \(5 T_\mathrm{H_2}=3 T_\mathrm{He}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{T_\mathrm{H_{2}}}{5}=\dfrac{T_\mathrm{{He }}}{3}\) |
Diatomic molecules like hydrogen have energies due to both translational as well as rotational motion. The equation in kinetic theory \(PV = \dfrac{2}{3}E,\) \(E\) is:
| 1. | the total energy per unit volume. |
| 2. | only the translational part of energy because rotational energy is very small compared to translational energy. |
| 3. | only the translational part of the energy because during collisions with the wall, pressure relates to change in linear momentum. |
| 4. | the translational part of the energy because rotational energies of molecules can be of either sign and its average over all the molecules is zero. |






