Volume, pressure, and temperature of an ideal gas are V, P, and T respectively. If the mass of its molecule is m, then its density is [k=boltzmann's constant]
(a) mkT (b)
(d) (d)
किसी आदर्श गैस के आयतन, दाब और तापमान क्रमशः V, P, और T हैं। यदि इसके अणु का द्रव्यमान m है, तब इसका घनत्व ज्ञात कीजिए [k = बोल्ट्समान नियतांक]:
(a) mkT (b)
(d) (d)
At constant volume, temperature is increased. Then
1. Collision on walls will be less
2. Number of collisions per unit time will increase
3. Collisions will be in straight lines
4. Collisions will not change
नियत आयतन पर, तापमान में वृद्धि की जाती है। तब:
1. दीवारों पर संघट्ट कम होगा।
2. प्रति एकांक समय में संघट्टों की संख्या बढ़ जाएगी।
3. संघट्ट सरल रेखाओं में होगें।
4. संघट्ट परिवर्तित नहीं होगें।
A gas mixture consists of molecules of type 1, 2 and 3, with molar masses and are the r.m.s. speed and average kinetic energy of the gases. Which of the following is true
1.
2.
3.
4.
किसी गैस मिश्रण में मोलर द्रव्यमान के साथ 1, 2 और 3 प्रकार के अणु सम्मिलित हैं। और गैसों की वर्ग माध्य मूल चाल और गतिज ऊर्जा हैं। निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा सत्य है?
1.
2.
3.
4.
The value of CV for one mole of neon gas is
1.
2.
3.
4.
निऑन गैस के एक मोल के लिए CV के मान की गणना कीजिए:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Five molecules of a gas have speeds, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 km. The value of the root mean square speed of the gas molecules is:
1. 3 km
2. km
3. km
4. 3.5 km
किसी गैस के पांच अणुओं का वेग 1, 2, 3, 4 और 5 km हैं। गैसीय अणुओं की वर्ग माध्य मूल चाल का मान ज्ञात कीजिए:
1. 3 km
2. km
3. km
4. 3.5 km
A vessel contains 1 mole of gas (molar mass 32) at a temperature T. The pressure of the gas is P. An identical vessel containing one mole of He gas (molar mass 4) at temperature 2T has a pressure of
1. P/8
2. P
3. 2P
4. 8P
T तापमान पर एक पात्र में (मोलर द्रव्यमान 32) गैस का 1 मोल है। गैस का दाब P है। 2T तापमान पर समान बर्तन जिसमें He गैस (मोलर द्रव्यमान 4) का एक मोल है, का दाब ज्ञात कीजिए:
1. P/8
2. P
3. 2P
4. 8P
The molecules of an ideal gas at a certain temperature have
1. Only potential energy
2. Only kinetic energy
3. Potential and kinetic energy both
4. None of the above
एक निश्चित तापमान पर किसी आदर्श गैस के अणुओं में होती है:
1. केवल स्थितिज ऊर्जा
2. केवल गतिज ऊर्जा
3. स्थितिज और गतिज ऊर्जा दोनों
4. उपरोक्त में से कोई नहीं
The mean free path for gas, with molecular diameter d and number density n, can be expressed as:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
एक गैस, जिसका आण्विक व्यास d तथा संख्या घनत्व n है, के लिए माध्य मुक्त पथ होगा:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
The figure shows a plot of PV/T versus P for of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
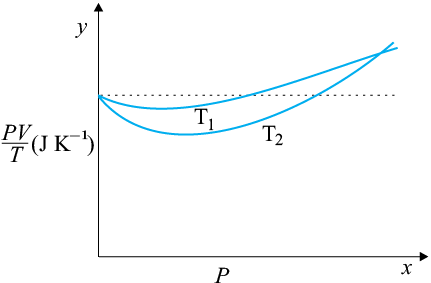
Then relation between
चित्र ऑक्सीजन गैस के दो विभिन्न तापमानों के लिए PV/T और P के मध्य एक आलेखन प्रदर्शित करता है।

के मध्य संबंध है:
A gaseous mixture contains equal number of hydrogen and nitrogen molecules. Specific heat measurements on this mixture at temperatures below 100 K would indicate that the value of (ratio of specific heats) for this mixture is
1. 3/2
2. 4/3
3. 5/3
4. 7/5
एक गैसीय मिश्रण में हाइड्रोजन और नाइट्रोजन अणुओं की समान संख्या होती है। 100 K से नीचे के तापमान पर इस मिश्रण पर विशिष्ट ऊष्मा की माप इंगित करेगी कि का मान इस मिश्रण के लिए (मिश्रण के लिए विशिष्ट ऊष्मा का अनुपात) है
1. 3/2
2. 4/3
3. 5/3
4. 7/5






